Siemens – Siemens Xcelerator: Festo joins the Siemens Industrial Edge Ecosystem
- Festo AX Data Access app available on the Siemens Industrial Edge Marketplace
- Connectivity solution helps to drive productivity and sustainability
- Siemens Industrial Edge Ecosystem continues to grow: More apps from Festo being planned
Siemens Xcelerator, the open digital business platform, creates an open ecosystem for collaboration between customers, Siemens, and certified partners, from large technology companies to independent software developers. Festo and Siemens announced their latest partnership at this year’s Hannover Messe trade fair. Festo has joined the Industrial Edge Ecosystem. To kick this off, Festo is offering the Festo AX Data access app, effective immediately, on the Siemens Industrial Edge Marketplace, where industrial customers can purchase numerous apps from different providers. The integrated IoT solutions based on these apps offer customers greater productivity, flexibility, and sustainability. Siemens launched the independent, cross-vendor app store for industrial customers in October 2021. This marketplace is based on the Siemens Industrial Edge platform. It uses edge computing to process data right at its source, such as on an industrial PC in machines or plants. Effective immediately, Festo is offering data-driven AI solutions from the Festo Automation Experience (Festo AX) portfolio on the marketplace.

Dr. Oliver Niese (Festo) and Rainer Brehm (Siemens) present the partnership at Hannover Messe 2023
Breakthrough for digital solutions in manufacturing
“We’re pleased to offer our Festo AX Industrial apps on the Siemens Industrial Edge platform as part of our partnership,” says Dr. Oliver Niese, who heads Digital Business at Festo. “This gives Festo an additional sales channel for industrial customers in the areas of mechanical engineering and production. Users benefit from the opportunity to purchase apps from different providers in a single place, to install them and run them at the machines on the shop floor.”
Another customer benefit is the wide range of software components that can be integrated into production in a standardized way. IoT solutions can even be scaled across lines and factories, thus considerably reducing manual software maintenance.
“At Siemens, we want to add even more partners to the Industrial Edge Ecosystem, especially those in the field of automation,” says Rainer Brehm, CEO of Factory Automation at Siemens. “A larger selection increases flexibility for our customers, who can build individual IoT solutions from Siemens and partner modules (Industrial Edge apps and devices). We create the greatest value for our customers when we work together across company boundaries.”
Analyzing data
Festo launched its Industrial Intelligence portfolio with the Festo AX Data Access connectivity solution, which feeds data from Festo components into Siemens Industrial Edge to supply analysis applications with data. Customers can build a monitoring solution based on the data and thereby improve maintenance processes, lower their energy consumption, and improve quality. Additional industrial apps from Festo are expected to be available on Siemens Industrial Edge, such as AI-based wear prediction for pneumatic drives.
Self-service solution improves flexibility
Festo AX Industrial apps like AX Data Access are building blocks that can be combined with other applications from Festo, Siemens, and third parties to form larger solutions. They enable production employees to independently build digital solutions for optimizing productivity. The partnership allows Festo and Siemens to support their customers on the path to becoming more sustainable, more flexible, and highly efficient.
For Festo AX Data Access on the Siemens Industrial Edge Marketplace please click here.
Further information on Industrial Edge is available here.
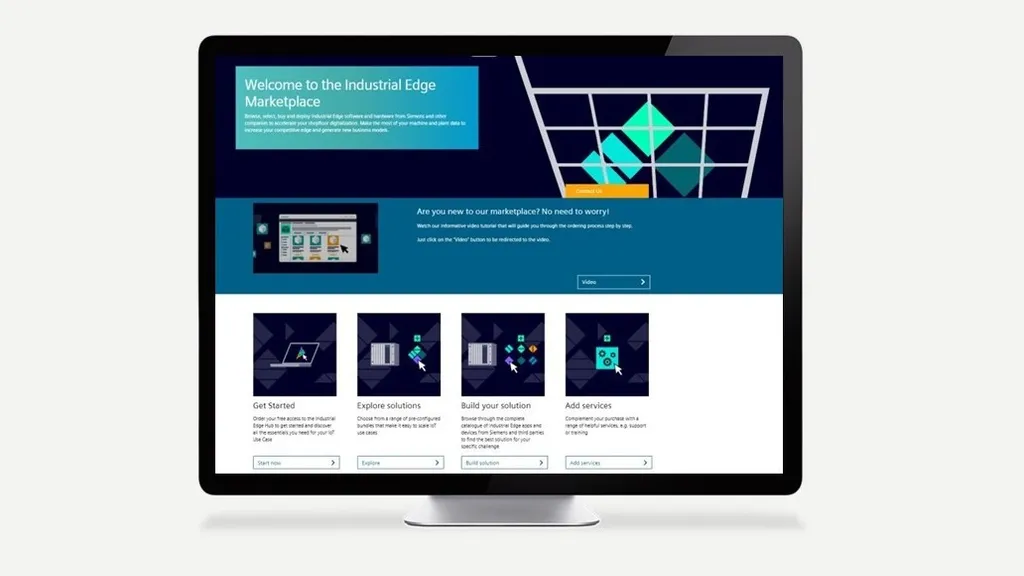
Siemens Industrial Edge Marketplace
SourceSIEMENS
EMR Analysis
More information on Siemens: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Dr. Roland Busch (President and Chief Executive Officer, Siemens AG): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Siemens Digital Industries (DI): See full profile on EMR Executive Services + https://new.siemens.com/global/en/company/about/businesses/digital-industries.html + Siemens DI is an innovation leader in automation and digitalization. Closely collaborating with partners and customers, DI drives the digital transformation in the process and discrete industries. With its Digital Enterprise portfolio, DI provides companies of all sizes with an end-to-end set of products, solutions and services to integrate and digitalize the entire value chain. Optimized for the specific needs of each industry, DI’s unique portfolio supports customers to achieve greater productivity and flexibility. DI is constantly adding innovations to its portfolio to integrate cutting-edge future technologies. Siemens Digital Industries has its global headquarters in Nuremberg, Germany, and has around 72,000 employees internationally.
More information on Cedrik Neike (Member of the Managing Board and Chief Executive Officer, Siemens Digital Industries, Siemens AG): See full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Xcelerator by Siemens: https://www.sw.siemens.com/en-US/digital-transformation/ + Xcelerator provides the engineering and manufacturing software, services and application development platform to blur the boundaries between industry domains. Companies can use this technology today to build the products of tomorrow. Turn complexity into your competitive advantage with Xcelerator.
Siemens Xcelerator consists of three pillars:
- Portfolio: A curated, modular portfolio of IOT-enabled hardware and software based on standard application programming interfaces, facilitating the integration of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT).
- Ecosystem: A growing ecosystem of partners.
- Marketplace: Interactions and transactions among customers, partners and developers.
More information on the Siemens Industrial Edge Marketplace: https://www.dex.siemens.com/?selected=edge + Browse, select, buy and deploy Industrial Edge software and hardware from Siemens and other companies to accelerate your shopfloor digitalization. Make the most of your machine and plant data to increase your competitive edge and generate new business models.
More information on Reiner Brehm (Chief Executive Officer, Factory Automation, Siemens Digital Industries, Siemens AG): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Festo: https://www.festo.com/ch/en/ + A responsible family-owned company and a global player in digitalisation.
Festo, the world’s leading supplier of automation technology and technical education, is deploying its products and services to meet the challenge of smart production for the future in the course of digitalisation. The company also relies on artificial intelligence and machine learning. Established in 1925, the independent family-owned company based in Esslingen aN., Germany, has been a driving force in automation for over 60 years and with its unique range of offers has become the world market leader in technical education. 300,000 customers worldwide in factory and process automation put their trust in the company’s pneumatic and electric drive solutions. In addition, Festo Didactic provides state-of-the-art training solutions for 56,000 industrial companies and educational institutions throughout the world. The Festo Group registered sales of €3.36 billion in the 2021 financial year and is represented at 250 locations throughout the world with a total of 20,700 employees. 7% of its annual turnover are invested in research and development.
- Founded: 1925 in Esslingen, Germany
- Turnover (Group): 3.81 billion euros
- Number of employees (Group): Around 20,800 employees worldwide
- Business divisions:
- Automation: automation technology
- Didactic: learning systems, training and consulting
- Festo customers:
- Automation: more than 300,000 industry customers in 176 countries
- Didactic: around 56,000 customers worldwide
- R&D investment:
- Around 7% of turnover
- Portfolio:
- Around 33,000 catalogue products in several hundred thousand variants
- Approximately 15,000 customised solutions per year
- Pneumatic, servo-pneumatic and electric automation technology
- LifeTech with medical technology and laboratory automation
- Industry-specific skills development solutions and industry consulting
- Companies:
- In about 60 countries
- Branch offices:
- Over 250 branch offices
- Distributors:
- Authorised representatives in a further 40 countries
- Worldwide service:
- In 176 countries
More information on Dipl.-Ing. Dr h.c. Oliver D. Jung (Chairman of the Management Board, Festo): https://www.festo.com/ch/en/e/about-festo/company/corporate-management-id_3694/
More information on Dr. Oliver Niese (Vice President, Digital Business, Festo): https://press.festo.com/de/technologies-and-products-1/dr-oliver-niese-1 + https://www.linkedin.com/in/dr-oliver-niese/
More information on HANNOVER MESSE 2023 (April 17-21, 2023, Hannover, Germany): https://www.hannovermesse.de/en/ + At the world’s leading trade fair for industry, some 4,000 companies from the mechanical engineering, electrical and digital industries as well as the energy sector will showcase technologies and solutions for a connected and climate-neutral industry. From the digitalization and automation of complex production processes and the use of hydrogen to power factories and the use of software to register and reduce carbon footprints.
EMR Additional Notes:
- IOT (The Internet Of Things):
- The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a system of interrelated, internet-connected objects that are able to collect and transfer data over a wireless network without human intervention.
- Describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet.
- The Most Popular IoT Devices are:
- Smart watches are the most popular IoT devices. …
- Gaming consoles. …
- Smart TV sets and content streaming devices. …
- Voice control devices. …
- Printers. …
- Cameras. …
- Lighting appliances. …
- Smart thermostats.
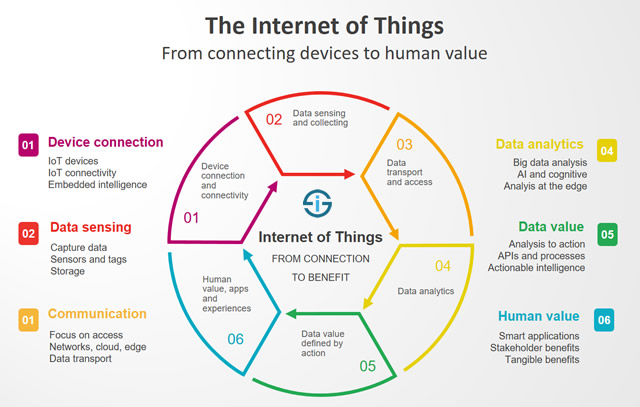

- Industrial IoT Solutions:
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) involves collecting and analyzing sensor-generated data to support equipment monitoring and maintenance, production process analytics and control, and more. In manufacturing IT since 1989, ScienceSoft offers IIoT consulting and development to create secure IIoT solutions.
- IT & OT:
- Information technology (IT) refers to anything related to computer technology, including hardware and software. Your email, for example, falls under the IT umbrella. This form of technology is less common in industrial settings, but often constitutes the technological backbone of most organizations and companies. These devices and programs have little autonomy and are updated frequently.
- Operational technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software used to change, monitor, or control physical devices, processes, and events within a company or organization. This form of technology is most commonly used in industrial settings, and the devices this technology refers to typically have more autonomy than information technology devices or programs. Examples of OT include SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition).
- => The main difference between OT and IT devices is that OT devices control the physical world, while IT systems manage data.
- Cloud Computing:
- Cloud computing is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the internet. … Cloud computing is a technology that uses the internet for storing and managing data on remote servers and then access data via the internet.
- Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center.
- Edge Computing:
- Edge computing is a form of computing that is done on site or near a particular data source, minimizing the need for data to be processed in a remote data center.
- Edge computing can enable more effective city traffic management. Examples of this include optimising bus frequency given fluctuations in demand, managing the opening and closing of extra lanes, and, in future, managing autonomous car flows.
- An edge device is any piece of hardware that controls data flow at the boundary between two networks. Edge devices fulfill a variety of roles, depending on what type of device they are, but they essentially serve as network entry — or exit — points.
- There are five main types of edge computing devices: IoT sensors, smart cameras, uCPE equipment, servers and processors. IoT sensors, smart cameras and uCPE equipment will reside on the customer premises, whereas servers and processors will reside in an edge computing data centre.
- In service-based industries such as the finance and e-commerce sector, edge computing devices also have roles to play. In this case, a smart phone, laptop, or tablet becomes the edge computing device.
- Edge Devices:
- Edge devices encompass a broad range of device types, including sensors, actuators and other endpoints, as well as IoT gateways. Within a local area network (LAN), switches in the access layer — that is, those connecting end-user devices to the aggregation layer — are sometimes called edge switches.
- Data Centers:
- A data center is a facility that centralizes an organization’s shared IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Because they house an organization’s most critical and proprietary assets, data centers are vital to the continuity of daily operations.
- Hyperscale Data Centers:
- The clue is in the name: hyperscale data centers are massive facilities built by companies with vast data processing and storage needs. These firms may derive their income directly from the applications or websites the equipment supports, or sell technology management services to third parties.
- Embedded PCs – Industrial PC (IPC):
- Embedded computer systems go by many names (Box PC, Gateway, Controller, Industrial PC, etc), but an Embedded PC is essentially any specialized computer system that is implemented as part of a larger device, intelligent system, or installation.
- Embedded Devices are less complex devices than Computers. Computers may be installed in other devices but are self-sufficient to exist. Embedded Devices only exist inside other Systems. Computers are more Difficult when used, compared to an Embedded System.


