Prysmian – Prysmian agrees framework agreement with Enedis to modernise the French power grid
- Prysmian is the partner selected by Enedis to supply the full range of medium-voltage cables to unlock a low-carbon power grid in France
- Prysmian will utilize its French factories in Gron and Montereau to ensure supply over a 7-year period of modernization for the French grid
Prysmian has signed a contract worth up to €550 million to become the supplier of the full range of medium-voltage cables for Enedis, over a seven-year period (2026-2032), which includes three optional years.
Prysmian has been a long-term partner to Enedis, and the signature reinforces French manufacturing excellence as Prysmian commits to supply cables from its Gron (Yonne) and Montereau-Fault-Yonne (Seine-et-Marne) sites.
Walking the talk – action to boost recycling of critical materials and a power grid that sets the European standard in low carbon emissions
Prysmian and Enedis share a common commitment to accelerating the adoption of circular business practices, such as using recycled materials – including critical materials such as base metals – and the overall reduction of carbon emissions across the grid thanks to renewables. The investment from Enedis includes specialized cables that can be easily integrated to the network to maximize the adoption of renewables in a simple, efficient and cost-effective way, bringing down overall carbon emissions – an area where France is already a European leader. This is fully in line with Prysmian’s strategic ambition to be Net-Zero in Scope 3 emissions by 2035.
As part of Prysmian’s ‘Accelerating Growth’ strategic plan, Prysmian is working to achieve over 55% of revenues from sustainable solutions by 2028, and this agreement will see the adoption of circular solutions in the cables. Prysmian will include over 12% of recycled aluminum and over 30% of recycled copper in the cables and will also adopt recycled polyethylene for the jacket material – which is the protective covering of the cables.
Prysmian has over 2,500 employees in France, as well as 4 R&D centers and 9 production facilities.
SourcePrysmian
EMR Analysis
More information on Prysmian: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Massimo Battaini (Group Chief Executive Officer and General Manager, Prysmian Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Pier Francesco Facchini (Chief Financial Officer and Executive Director, Finance, Administration, Control and IT, Prysmian): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Enedis: https://www.enedis.fr/ + Enedis is a public service company that manages France’s electricity distribution network, employing 41,000 people. Serving 38.8 million customers, it develops, operates and modernises 1.4 million kilometres of low- and medium-voltage networks (230 and 20,000 volts), as well as managing the associated data. Enedis connects customers to the grid, provides 24/7 outage response, carries out electricity metering (for both production and consumption) and performs all related technical operations. Acting on behalf of local authorities, which own the distribution networks, Enedis is independent from energy suppliers, who are responsible for selling and managing electricity supply contracts. A mission-driven company since June 2023, Enedis’ purpose is to “work towards an innovative, efficient, and socially responsible public electricity distribution service, connecting society to the collective challenge of a sustainable world.”
- 41K Employees
- 1,4M kilometers of electric lines
- 38,5M customers
More information on Marianne Laigneau (Chairman of the Management Board, Enedis): https://www.enedis.fr/nous-connaitre/notre-gouvernance + https://www.linkedin.com/in/marianne-laigneau/?locale=en_US
More information on Net Zero by 2050 by the United Nations: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/net-zero-coalition + Put simply, net zero means cutting greenhouse gas emissions to as close to zero as possible, with any remaining emissions re-absorbed from the atmosphere, by oceans and forests for instance.
Currently, the Earth is already about 1.1°C warmer than it was in the late 1800s, and emissions continue to rise. To keep global warming to no more than 1.5°C – as called for in the Paris Agreement – emissions need to be reduced by 45% by 2030 and reach net zero by 2050.
More than 140 countries, including the biggest polluters – China, the United States, India and the European Union – have set a net-zero target, covering about 88% of global emissions. More than 9,000 companies, over 1000 cities, more than 1000 educational institutions, and over 600 financial institutions have joined the Race to Zero, pledging to take rigorous, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030.
More information on Net Zero by 2050 by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi): https://sciencebasedtargets.org/net-zero + The SBTi’s Corporate Net-Zero Standard is the world’s only framework for corporate net-zero target setting in line with climate science. It includes the guidance, criteria, and recommendations companies need to set science-based net-zero targets consistent with limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
UN vs. SBTi:
- UN targets nations, while SBTi focuses on companies. UN sets a broad goal, while SBTI provides a detailed framework for target setting.
- Both aim to achieve net zero emissions and limit warming to 1.5°C. The UN sets the overall direction, and SBTi helps businesses translate that goal into actionable plans.
Key components of the Corporate Net-Zero Standard:
- Near-term targets: Rapid, deep cuts to direct and indirect value-chain emissions must be the overarching priority for companies. Companies must set near-term science-based targets to roughly halve emission before 2030. This is the most effective, scientifically-sound way of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
- Long-term targets: Companies must set long-term science-based targets. Companies must cut all possible – usually more than 90% – of emissions before 2050.
- Neutralize residual emissions: After a company has achieved its long-term target and cut emissions by more than 90%, it must use permanent carbon removal and storage to counterbalance the final 10% or more of residual emissions that cannot be eliminated. A company is only considered to have reached net-zero when it has achieved its long-term science-based target and neutralized any residual emissions.
- Beyond Value Chain Mitigation (BVCM): Businesses should invest now in actions to reduce and remove emissions outside of their value chains in addition to near- and long-term science-based targets.
EMR Additional Notes:
- Grid, Microgrids, DERs and DERM’s:
- Grid / Power Grid:
- The power grid is a network for delivering electricity to consumers. The power grid includes generator stations, transmission lines and towers, and individual consumer distribution lines.
- The grid constantly balances the supply and demand for the energy that powers everything from industry to household appliances.
- Electric grids perform three major functions: power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- The power grid is a network for delivering electricity to consumers. The power grid includes generator stations, transmission lines and towers, and individual consumer distribution lines.
- Microgrid:
- Small-scale power grid that can operate independently or collaboratively with other small power grids. The practice of using microgrids is known as distributed, dispersed, decentralized, district or embedded energy production.
- Smart Grid:
- Any electrical grid + IT at all levels.
- Micro Grid:
- Group of interconnected loads and DERs (Distributed Energy Resources) within a clearly defined electrical and geographical boundaries witch acts as a single controllable entity with respect to the main grid.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs):
- Small-scale electricity supply (typically in the range of 3 kW to 50 MW) or demand resources that are interconnected to the electric grid. They are power generation resources and are usually located close to load centers, and can be used individually or in aggregate to provide value to the grid.
- Common examples of DERs include rooftop solar PV units, natural gas turbines, microturbines, wind turbines, biomass generators, fuel cells, tri-generation units, battery storage, electric vehicles (EV) and EV chargers, and demand response applications.
- Small-scale electricity supply (typically in the range of 3 kW to 50 MW) or demand resources that are interconnected to the electric grid. They are power generation resources and are usually located close to load centers, and can be used individually or in aggregate to provide value to the grid.
- Distributed Energy Resources Management Systems (DERMS):
- Platforms which helps mostly distribution system operators (DSO) manage their grids that are mainly based on distributed energy resources (DER).
- DERMS are used by utilities and other energy companies to aggregate a large energy load for participation in the demand response market. DERMS can be defined in many ways, depending on the use case and underlying energy asset.
- Platforms which helps mostly distribution system operators (DSO) manage their grids that are mainly based on distributed energy resources (DER).
- Grid / Power Grid:
- Extra Low-Voltage (ELV):
- Extra-Low Voltage (ELV) is defined as a voltage of 50V or less (AC RMS), or 120V or less (ripple-free DC).
- Low-Voltage (LV):
- The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) defines Low Voltage (LV) for supply systems as voltage in the range 50–1000 V AC or 120–1500 V DC.
- Medium-Voltage (MV):
- Medium Voltage (MV) is a voltage class that typically falls between low voltage and high voltage, with a common range being from 1 kV to 35 kV. In some contexts, this range can extend higher, up to 69 kV.
- High-Voltage (HV):
- The International Electrotechnical Commission define high voltage as above 1000 V for alternating current, and at least 1500 V for direct current.
- Super High-Voltage or Extra High-Voltage (EHV):
- Super High-Voltage or Extra High-Voltage (EHV) is the voltage class used for long-distance bulk power transmission. The range for EHV systems is typically from 230 kV to 800 kV.
- Ultra High-Voltage (UHV):
- Ultra High-Voltage (UHV) is the highest voltage class used in electrical transmission, defined as a voltage of 1000 kV or greater.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- The primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle.
- Biogenic Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Biogenic Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) are the same molecule. Scientists differentiate between biogenic carbon (that which is absorbed, stored and emitted by organic matter like soil, trees, plants and grasses) and non-biogenic carbon (that found in all other sources, most notably in fossil fuels like oil, coal and gas).
- CO2e (Carbon Dioxide Equivalent):
- CO2e means “carbon dioxide equivalent”. In layman’s terms, CO2e is a measurement of the total greenhouse gases emitted, expressed in terms of the equivalent measurement of carbon dioxide. On the other hand, CO2 only measures carbon emissions and does not account for any other greenhouse gases.
- A carbon dioxide equivalent or CO2 equivalent, abbreviated as CO2-eq is a metric measure used to compare the emissions from various greenhouse gases on the basis of their global-warming potential (GWP), by converting amounts of other gases to the equivalent amount of carbon dioxide with the same global warming potential.
- Carbon dioxide equivalents are commonly expressed as million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents, abbreviated as MMTCDE.
- The carbon dioxide equivalent for a gas is derived by multiplying the tonnes of the gas by the associated GWP: MMTCDE = (million metric tonnes of a gas) * (GWP of the gas).
- For example, the GWP for methane is 25 and for nitrous oxide 298. This means that emissions of 1 million metric tonnes of methane and nitrous oxide respectively is equivalent to emissions of 25 and 298 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide.
- Carbon Footprint:
- There is no universally agreed definition of what a carbon footprint is.
- A carbon footprint is generally understood to be the total amount of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that are directly or indirectly caused by an individual, organization, product, or service. These emissions are typically measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e).
- In 2009, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) published a standard for calculating and reporting corporate carbon footprints. This standard is widely accepted by businesses and other organizations around the world. The GHG Protocol defines a carbon footprint as “the total set of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, directly and indirectly, through its own operations and the value chain.”
- Decarbonization:
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions through the use of low carbon power sources, and achieving a lower output of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Carbon Credits or Carbon Offsets:
- Permits that allow the owner to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit permits the emission of one ton of carbon dioxide or the equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
- The carbon credit is half of a so-called cap-and-trade program. Companies that pollute are awarded credits that allow them to continue to pollute up to a certain limit, which is reduced periodically. Meanwhile, the company may sell any unneeded credits to another company that needs them. Private companies are thus doubly incentivized to reduce greenhouse emissions. First, they must spend money on extra credits if their emissions exceed the cap. Second, they can make money by reducing their emissions and selling their excess allowances.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) – Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS):
- CCS involves the capture of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes. This carbon is then transported from where it was produced, via ship or in a pipeline, and stored deep underground in geological formations.
- CCS projects typically target 90 percent efficiency, meaning that 90 percent of the carbon dioxide from the power plant will be captured and stored.
- CCUS adds the utilization aspect, where the captured CO2 is used as a new product or raw material.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) or Durable Carbon Removal:
- Carbon Dioxide Removal encompasses approaches and methods for removing CO2 from the atmosphere and then storing it permanently in underground geological formations, in biomass, oceanic reservoirs or long-lived products in order to achieve negative emissions.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC):
- Technologies that extract CO2 directly from the atmosphere at any location, unlike carbon capture which is generally carried out at the point of emissions, such as a steel plant.
- Constraints like costs and energy requirements as well as the potential for pollution make DAC a less desirable option for CO2 reduction. Its larger land footprint when compared to other mitigation strategies like carbon capture and storage systems (CCS) also put it at a disadvantage.
- Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACCS):
- Climate technology that removes carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the ambient atmosphere using large fans and chemical processes to bind with the CO2.
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS):
- Negative emissions technology that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) from biomass used for energy production and stores it permanently. Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere as they grow (photosynthesis), and BECCS interrupts the cycle by capturing this biogenic CO2 during the energy conversion process—burning, fermentation, etc.—instead of letting it re-enter the atmosphere.
- Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW):
- Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technique that accelerates the natural process of rock weathering by grinding silicate rocks into dust and spreading it on land, typically agricultural fields. This process uses rainwater to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into mineral carbonates, which are then stored long-term in soils, groundwater, and oceans.
- Limits of Carbon Dioxide Storage:
- Carbon storage is not endless; the Earth’s capacity for permanently storing vast amounts of captured carbon, particularly in geological formations, is limited, potentially reaching a critical limit of 1,460 gigatonnes at around 2200, though storage durations vary significantly depending on the method, from decades for some biological methods to potentially millions of years for others like mineralization. While some methods offer very long-term storage, the sheer volume needed to meet climate targets requires scaling up storage significantly beyond current capacity, raising concerns about the available volume over time.
- Global Warming:
- Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere.
- Global Warming Potential (GWP):
- The heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, as a multiple of the heat that would be absorbed by the same mass of carbon dioxide (CO2). GWP is 1 for CO2. For other gases it depends on the gas and the time frame.
- Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e or CO2eq or CO2-e) is calculated from GWP. For any gas, it is the mass of CO2 which would warm the earth as much as the mass of that gas. Thus it provides a common scale for measuring the climate effects of different gases. It is calculated as GWP times mass of the other gas. For example, if a gas has GWP of 100, two tonnes of the gas have CO2e of 200 tonnes.
- GWP was developed to allow comparisons of the global warming impacts of different gases.
- Greenhouse Gas (GHG):
- A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere. By increasing the heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect, which ultimately leads to global warming.
- The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor (which all occur naturally), and fluorinated gases (which are synthetic).
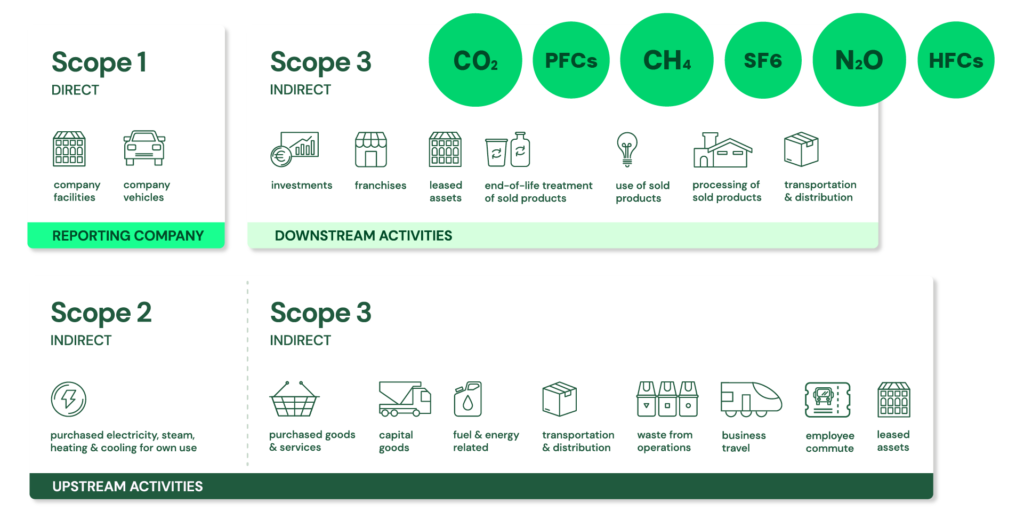
- GHG Protocol Corporate Standard Scope 1, 2 and 3: https://ghgprotocol.org/ + The GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard provides requirements and guidance for companies and other organizations preparing a corporate-level GHG emissions inventory. Scope 1 and 2 are typically mandatory for companies that are required to report their emissions by national or regional regulations. The GHG Protocol itself is a voluntary standard.
- Scope 1: Direct emissions:
- Direct emissions from company-owned and controlled resources. In other words, emissions are released into the atmosphere as a direct result of a set of activities, at a firm level. It is divided into four categories:
- Stationary combustion (e.g from fuels, heating sources). All fuels that produce GHG emissions must be included in scope 1.
- Mobile combustion is all vehicles owned or controlled by a firm, burning fuel (e.g. cars, vans, trucks). The increasing use of “electric” vehicles (EVs), means that some of the organisation’s fleets could fall into Scope 2 emissions.
- Fugitive emissions are leaks from greenhouse gases (e.g. refrigeration, air conditioning units). It is important to note that refrigerant gases are a thousand times more dangerous than CO2 emissions. Companies are encouraged to report these emissions.
- Process emissions are released during industrial processes, and on-site manufacturing (e.g. production of CO2 during cement manufacturing, factory fumes, chemicals).
- Direct emissions from company-owned and controlled resources. In other words, emissions are released into the atmosphere as a direct result of a set of activities, at a firm level. It is divided into four categories:
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions – owned:
- Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy, from a utility provider. In other words, all GHG emissions released in the atmosphere, from the consumption of purchased electricity, steam, heat and cooling. For most organisations, electricity will be the unique source of scope 2 emissions. Simply stated, the energy consumed falls into two scopes: Scope 2 covers the electricity consumed by the end-user. Scope 3 covers the energy used by the utilities during transmission and distribution (T&D losses).
- Scope 3: Indirect emissions – not owned:
- Indirect emissions – not included in scope 2 – that occur in the value chain of the reporting company, including both upstream and downstream emissions. In other words, emissions are linked to the company’s operations. According to the GHG protocol, scope 3 emissions are separated into 15 categories.
- Scope 1: Direct emissions:
- Circular Economy:
- A circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development designed to benefit businesses, society, and the environment. In contrast to the ‘take-make-waste’ linear model, a circular economy is regenerative by design and aims to gradually decouple growth from the consumption of finite resources.
- In such an economy, all forms of waste, such as clothes, scrap metal and obsolete electronics, are returned to the economy or used more efficiently.
- The aim of a circular economy is hence to create a closed-loop system where waste and pollution are minimized and resources are conserved, reducing the environmental impact of production and consumption.
- Sustainability Vs. Circular Economy:
- Circularity focuses on resource cycles, while sustainability is more broadly related to people, the planet and the economy. Circularity and sustainability stand in a long tradition of related visions, models and theories.
- A sustainable circular economy involves designing and promoting products that last and that can be reused, repaired and remanufactured. This retains the functional value of products, rather than just recovering the energy or materials they contain and continuously making products anew.
- Olefin (Alkene) & Polyolefin:
- Olefins are a class of chemicals made up of hydrogen and carbon with one or more pairs of carbon atoms linked by a double bond. Ethylene, propylene and 1,3-butadiene are examples of olefins.
- Also called an alkene, a compound made up of hydrogen and carbon that contains one or more pairs of carbon atoms linked by a double bond. Olefins are examples of unsaturated hydrocarbons (compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon and at least one double or triple bond).
- Polyolefins are a family of thermoplastics that include polyethylene and polypropylene. They are produced by polymerizing, respectively, ethylene and propylene, which are mainly obtained from oil and natural gas but can also be derived from renewable resources (e.g., sugar cane).
- Polyethylene (PE) & High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- Polyethylene (PE) is a thermoplastic polymer considered one of the most versatile plastic materials available today. It is used to manufacture numerous items, including food and beverage containers, cleaning product bottles, pipes, cutting boards, and some shoe parts.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is a specific type of PE. It is hard-wearing and does not break down under exposure to sunlight. It can withstand more extreme temperatures than PET, both hot and cold. HDPE can be reused and recycled.
- Polypropylene (PP):
- Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic “addition polymer” made from the combination of propylene monomers. It is a low-density, stress-resistant thermoplastic. It is a rigid, semi-crystalline thermoplastic that was first polymerized in 1951 and is used widely today in a range of domestic and industrial applications.
- Polypropylene is a plastic. Of the commercial plastics on the market today, polypropylene is considered one of the safest.
- Polypropylene uses range from plastic packaging, plastic parts for machinery and equipment and even fibres and textiles.
- Polyamide (PA):
- A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
- Synthetic polymer of a type made by the linkage of an amino group of one molecule and a carboxylic acid group of another, including many synthetic fibres such as nylon.
- Nylon is low-friction, more malleable, and can withstand higher temperatures, making it ideal for prototyping and manufacturing components that will be subject to resistance. Polypropylene is generally stronger than many nylons and more resistant to physical stress, making it ideal for high-resistance equipment.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC or Vinyl):
- High strength thermoplastic material widely used in applications, such as pipes, medical devices, wire and cable insulation…the list is endless. It is the world’s third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic. About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid and flexible. The rigid form of PVC is used in construction for pipe and in profile applications such as doors and windows.
- Vinyl is commonly used as a shorthand name for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastic.
- Polyester (PET):
- Synthetic resin in which the polymer units are linked by ester groups, used chiefly to make synthetic textile fibres.
- Synthetic fabric that’s usually derived from petroleum. This fabric is one of the world’s most popular textiles, and it is used in thousands of different consumer and industrial applications. Chemically, polyester is a polymer primarily composed of compounds within the ester functional group.
- Polyester GRP:
- Glass Reinforced Polyester (GRP) is a polyester material reinforced with the addition of glass fibre.
- GRP is made up of a combination of glass fibre and polymer or plastic. It has many desirable properties which include: High strength to weight ratio and excellent durability.
- GRP stands for Glass Reinforced Plastic (or Polymer). You may also know it as FRP (Fibre Reinforced Plastic) or even as Fiberglass. It is a blend of a thermosetting plastic resin (such as polyester) and recycled glass with a tough waterproof resin to bond it all together.


