Hikvision – Hikvision unveils WonderHub and elevates smart collaboration across industries
November 15, 2024 – Hikvision unveiled its fully upgraded smart collaboration business.
The event showcased a range of innovative products designed to transform collaboration in education, meetings, retail, and more. Among the highlights were cutting-edge solutions like WonderHub interactive displays, digital signage, and video conference devices. These products underscore Hikvision’s commitment to driving digital transformation and enhancing user experiences in an increasingly connected world.
At the heart of this ecosystem is WonderHub, which features WonderOS, an AI-powered platform that seamlessly connects devices and enhances collaboration. With tools like WonderSpark for interactive whiteboards and WonderCast for wireless content sharing, WonderHub enables users to communicate, create, and collaborate more effectively than ever.

Boosting Classroom Engagement with Innovative Solutions
In education, WonderHub is designed to elevate classroom experiences. The interactive displays enable students to share and express ideas effortlessly, creating a more engaging and dynamic learning environment. The built-in WonderSpark smart whiteboard software uses AI to recognize equations, provide solutions, and generate interactive 3D teaching materials across subjects like mathematics, chemistry, and natural sciences. Teachers can also access licensed images and videos through Creative Commons integration, enriching lesson content and boosting student engagement.
Classrooms equipped with WonderHub also benefit from multi-window modes and a suite of 19 educational tools. These include subject-specific templates and interactive applications. For remote learning, WonderHub integrates seamlessly with third-party conferencing platforms, allowing students to collaborate in real-time, no matter their location.
Empowering Business Meetings with Intelligent Features
Hikvision’s smart collaboration solutions transform business meetings into more efficient and immersive experiences. The WonderHub Ultra Series allows users to easily connect personal devices and leverage the interactive display’s camera, speakers, and microphone for high-quality remote conferencing. The HiSpire meeting management system streamlines meeting logistics, including room scheduling, attendee notifications, post-meeting summaries, and distribution of materials.
Advanced AI features, such as auto-framing and speaker tracking, ensure optimal video quality. Meanwhile, app-free screen casting allows for easy sharing of presentation materials. The X12 and X28 audio-video cameras offer enterprises tailored setups to suit meeting rooms of any size, ensuring seamless communication with high-definition video and precise audio capture.
Transforming Retail Spaces with Dynamic Digital Signage
Hikvision has also advanced its digital signage solutions to enhance customer engagement in retail scenarios. The vibrant displays and centralized content management allow retailers to effectively capture attention. High-brightness window displays attract passersby with promotions and new product highlights. Meanwhile, floor-standing signage supports interactive features, such as self-service ordering. The HikCentral FocSign platform enables retailers to remotely manage and distribute content across multiple locations, improving operational efficiency and ensuring consistent branding.
These digital signage solutions, including the DP and DL series, boast superior brightness and clarity, ensuring visibility even in strong lighting conditions. The displays run on Hikvision’s self-developed platform and support WonderCast wireless casting, enabling quick and easy content sharing from various devices.
Since entering the smart collaboration market in 2017, Hikvision has rapidly become a leading global player. With over 300,000 units sold across more than 140 countries and regions, Hikvision’s smart collaboration business exemplifies the company’s commitment to innovation, quality, and user-centric design. As a key highlight of this evolution, the fully upgraded WonderHub represents the next leap forward in smart collaboration technology.
By bridging advanced technology with practical applications, WonderHub, along with Hikvision’s broader range of smart collaboration solutions, is leading the way in providing more efficient and intelligent solutions for users worldwide.
For more information about Hikvision’s smart collaboration products and solutions, please visit Hikvision’s official website.
SourceHikvision
EMR Analysis
More information on HikVision: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Hu Yangzhong (President & Chief Executive Officer, Hikvision): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on WonderHub by HikVision: https://ifpd.hikvision.com/wonderhub/v7-exclusive.html + Integrated design makes maintenance easier: The whole machine is designed in one piece, no other external wires are required except the power cord, which effectively saves space
Reduce the risk of improper operation and improve operational stability; front maintenance design makes daily maintenance more convenient
WonderHub by Hikvision is an advanced smart collaboration platform designed to enhance communication and interaction across various sectors, including education, business, and retail. Introduced in November 2024, it integrates AI-driven tools and interactive displays to create more engaging and efficient environments.
EMR Additional Notes:
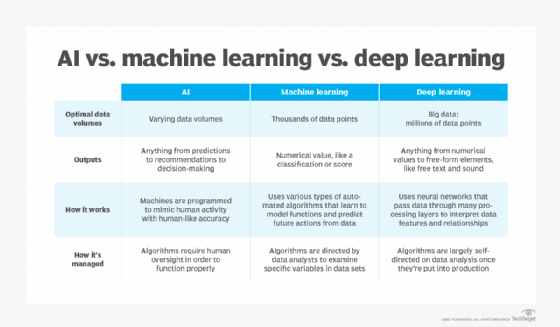
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but well a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
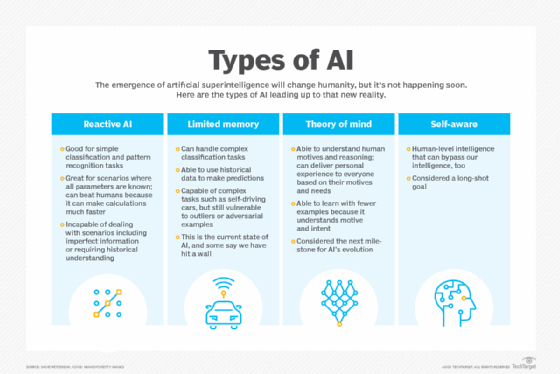
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
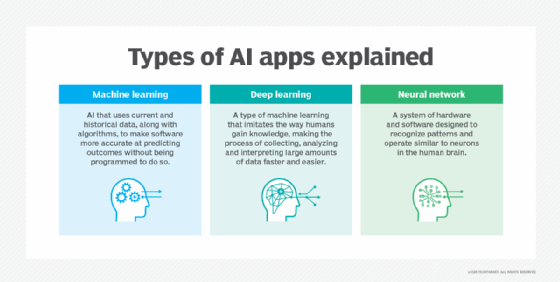
- Machine Learning (ML):
- Developed to mimic human intelligence, it lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data, statistics formulas and detecting patterns.
- ML allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
- ML algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for ML. Other uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, business process automation (BPA) and predictive maintenance.
- Classical ML is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning (DL):
- Subset of machine learning, Deep Learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with ML. Face recognition is a good example.
- DL makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. DL demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- DL is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision (CV):
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
- Machine Vision (MV):
- Machine Vision is the ability of a computer to see; it employs one or more video cameras, analog-to-digital conversion and digital signal processing. The resulting data goes to a computer or robot controller. Machine Vision is similar in complexity to Voice Recognition.
- MV uses the latest AI technologies to give industrial equipment the ability to see and analyze tasks in smart manufacturing, quality control, and worker safety.
- Computer Vision systems can gain valuable information from images, videos, and other visuals, whereas Machine Vision systems rely on the image captured by the system’s camera. Another difference is that Computer Vision systems are commonly used to extract and use as much data as possible about an object.
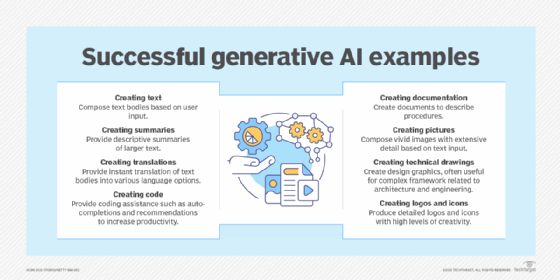
- Generative AI (GenAI):
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Edge AI Technology:
- Edge artificial intelligence refers to the deployment of AI algorithms and AI models directly on local edge devices such as sensors or Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which enables real-time data processing and analysis without constant reliance on cloud infrastructure.
- Simply stated, edge AI, or “AI on the edge“, refers to the combination of edge computing and artificial intelligence to execute machine learning tasks directly on interconnected edge devices. Edge computing allows for data to be stored close to the device location, and AI algorithms enable the data to be processed right on the network edge, with or without an internet connection. This facilitates the processing of data within milliseconds, providing real-time feedback.
- Self-driving cars, wearable devices, security cameras, and smart home appliances are among the technologies that leverage edge AI capabilities to promptly deliver users with real-time information when it is most essential.
- Multimodal Intelligence and Agents:
- Subset of artificial intelligence that integrates information from various modalities, such as text, images, audio, and video, to build more accurate and comprehensive AI models.
- Multimodal capabilities allows to interact with users in a more natural and intuitive way. It can see, hear and speak, which means that users can provide input and receive responses in a variety of ways.
- An AI agent is a computational entity designed to act independently. It performs specific tasks autonomously by making decisions based on its environment, inputs, and a predefined goal. What separates an AI agent from an AI model is the ability to act. There are many different kinds of agents such as reactive agents and proactive agents. Agents can also act in fixed and dynamic environments. Additionally, more sophisticated applications of agents involve utilizing agents to handle data in various formats, known as multimodal agents and deploying multiple agents to tackle complex problems.


